Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs)
CVEs are weaknesses in software that can be exploited to access sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers. Because modern software is complex with its many layers, interdependencies, data inputs, and libraries, vulnerabilities tend to emerge over time. Knowing when and how the code you use is vulnerable to attacks is a powerful tool in allowing you to mitigate the potential for harm, and Package Security Manager provides you with everything you need to keep your pipeline secure.
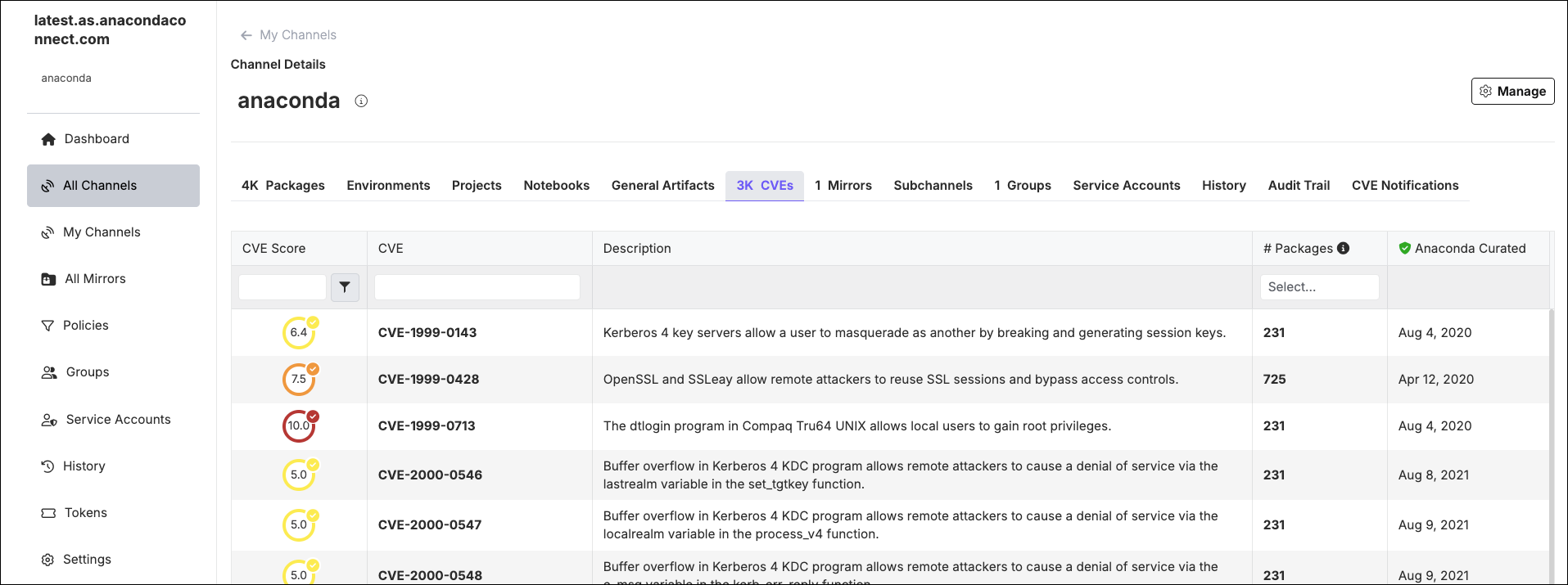
 To view all CVEs associated with a channel, open the channel’s page and select the CVEs tab.
The number shown in the CVEs tab is the total number of CVEs associated with the packages contained in the channel. CVEs are listed alphanumerically by name and show how many packages in the channel are affected by each CVE.
To view all CVEs associated with a channel, open the channel’s page and select the CVEs tab.
The number shown in the CVEs tab is the total number of CVEs associated with the packages contained in the channel. CVEs are listed alphanumerically by name and show how many packages in the channel are affected by each CVE.
 Select a package, then select the CVEs tab to view details regarding its associated CVEs. Apply filters to your package’s CVEs tab by utilizing the fields at the top of the table columns. You can filter by:
Select a package, then select the CVEs tab to view details regarding its associated CVEs. Apply filters to your package’s CVEs tab by utilizing the fields at the top of the table columns. You can filter by:
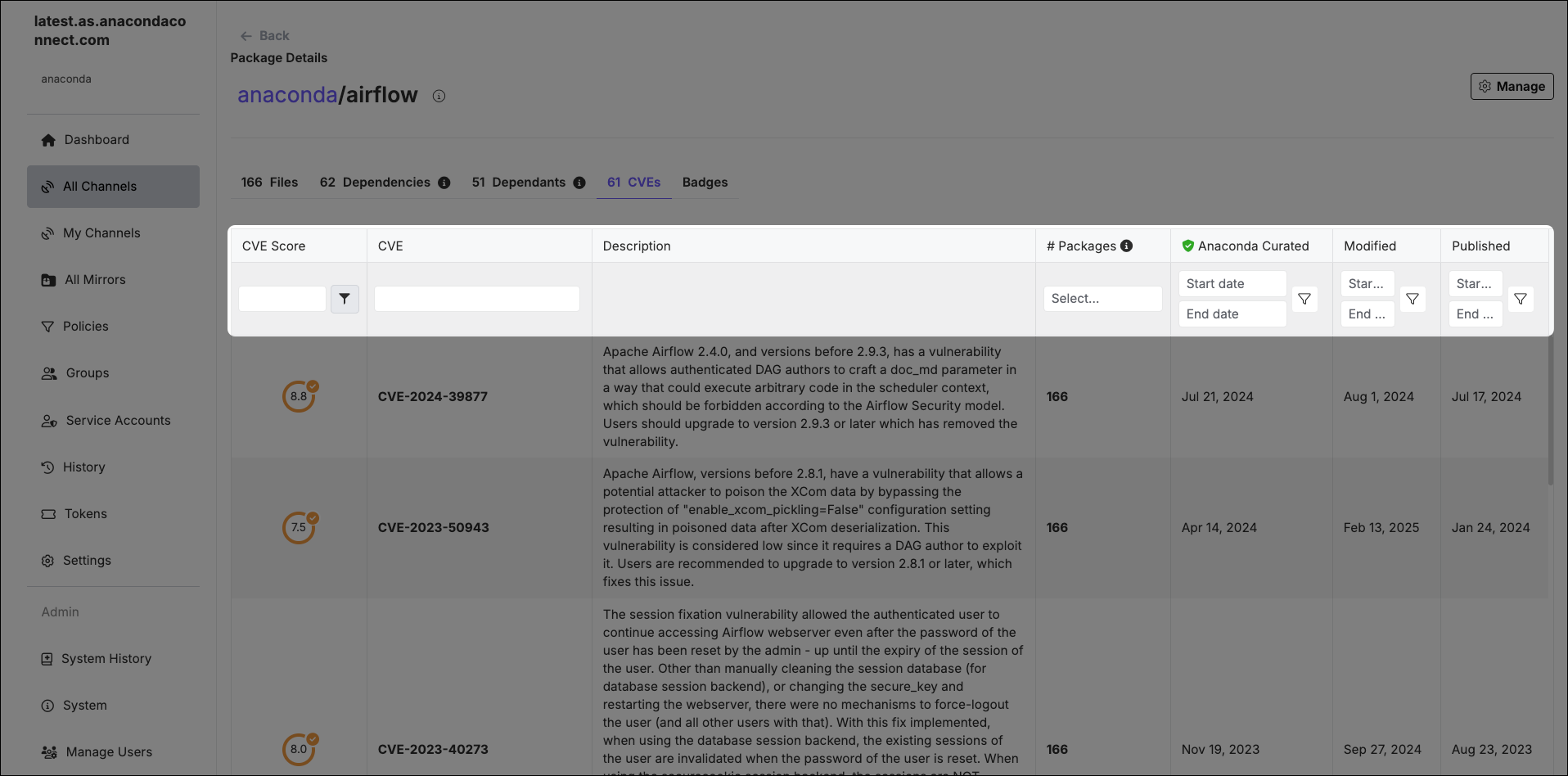 The CVE Score column shows the highest CVE Score of the associated active and reported CVEs. If no active or reported CVEs are found, the highest score for cleared, disputed, or mitigated CVEs are displayed.
The CVE Score column shows the highest CVE Score of the associated active and reported CVEs. If no active or reported CVEs are found, the highest score for cleared, disputed, or mitigated CVEs are displayed.
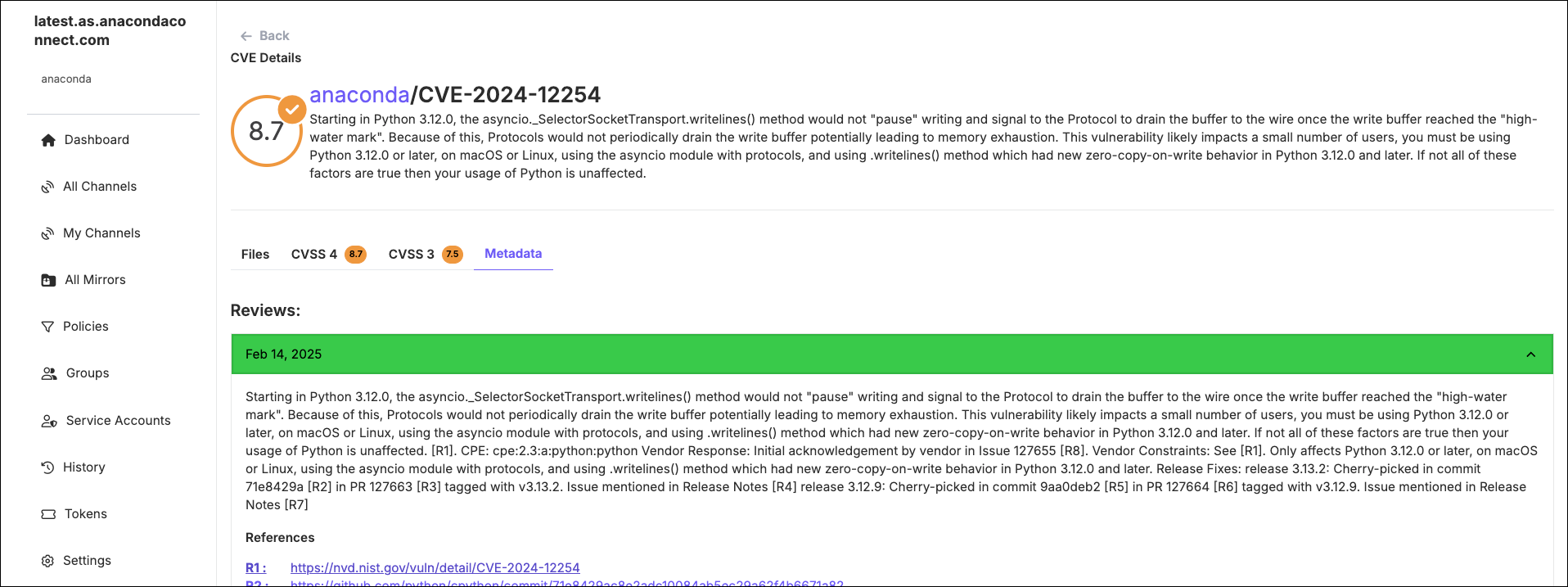
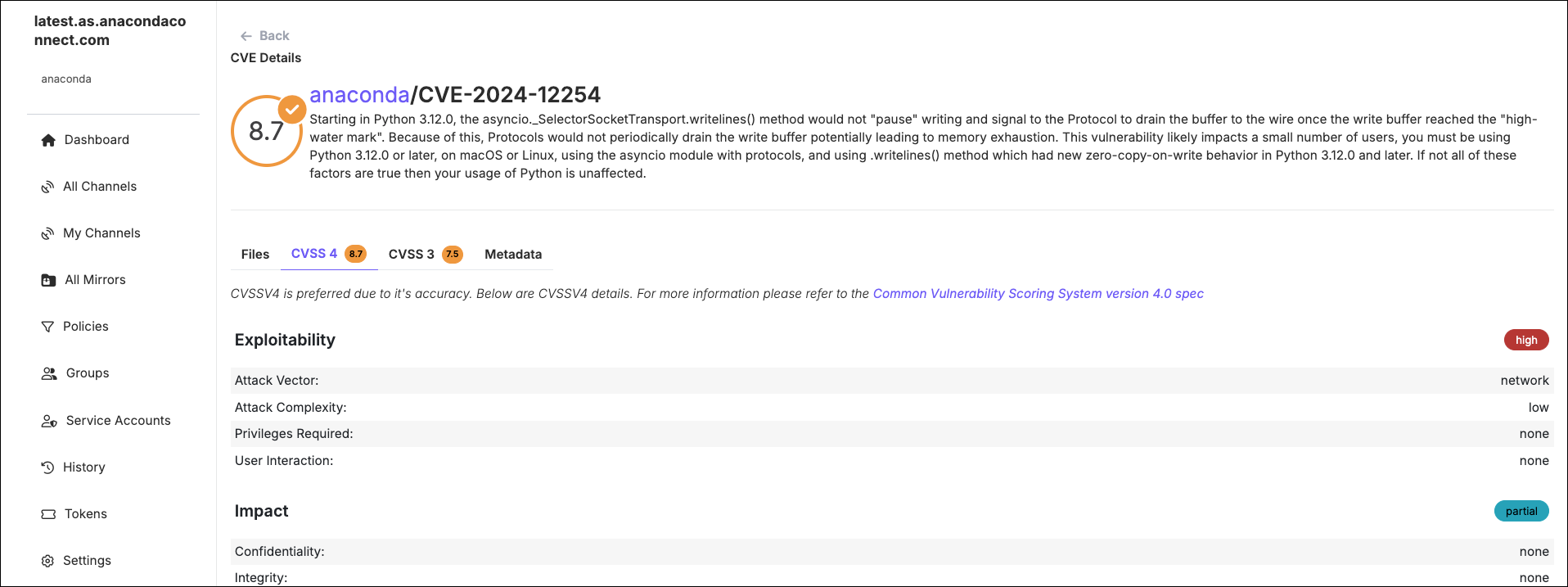 Select the Metadata tab to view Anaconda’s review of the CVE. The review contains references used to support the review and curate the CVE.
Select the Metadata tab to view Anaconda’s review of the CVE. The review contains references used to support the review and curate the CVE.
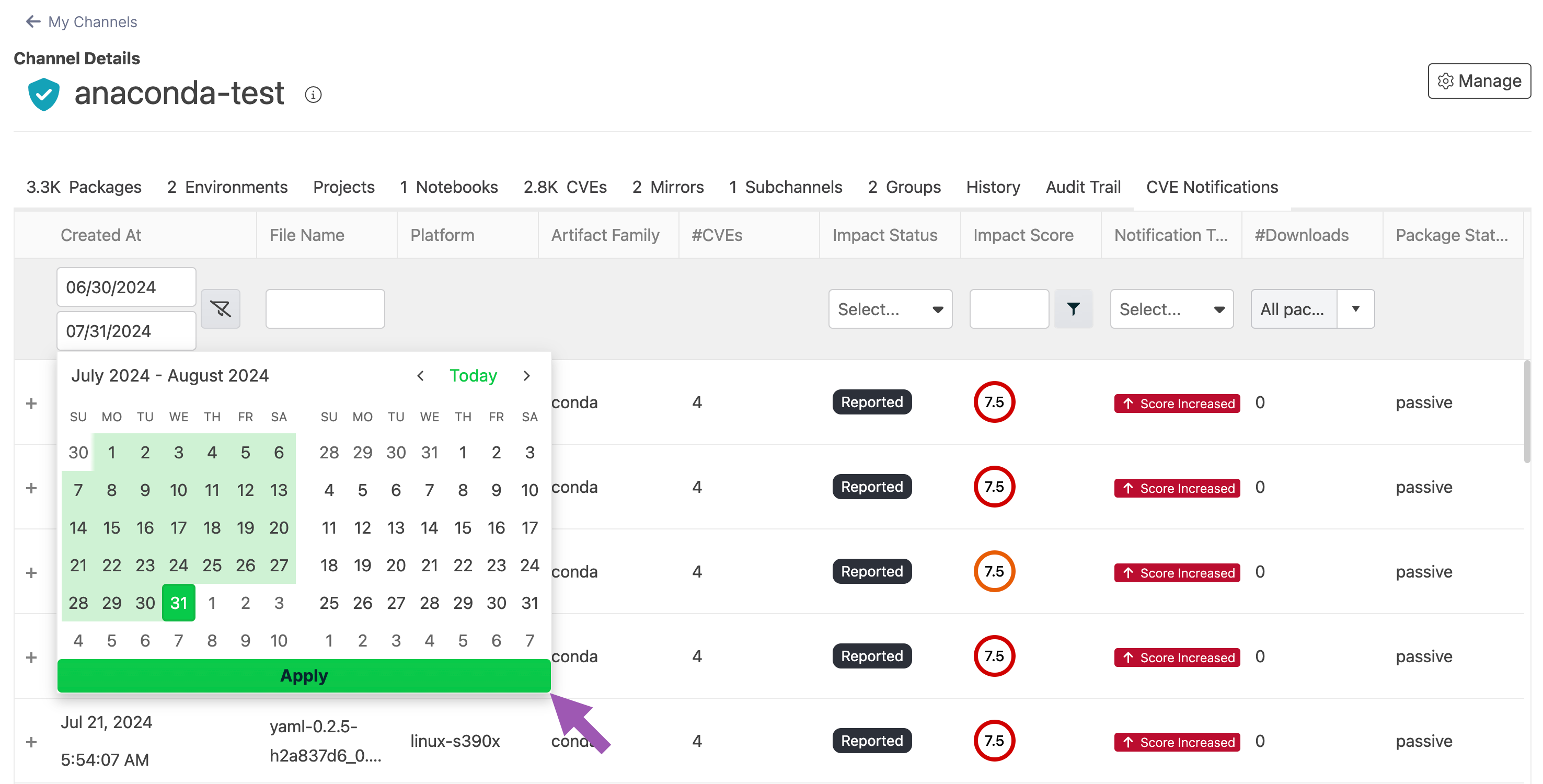
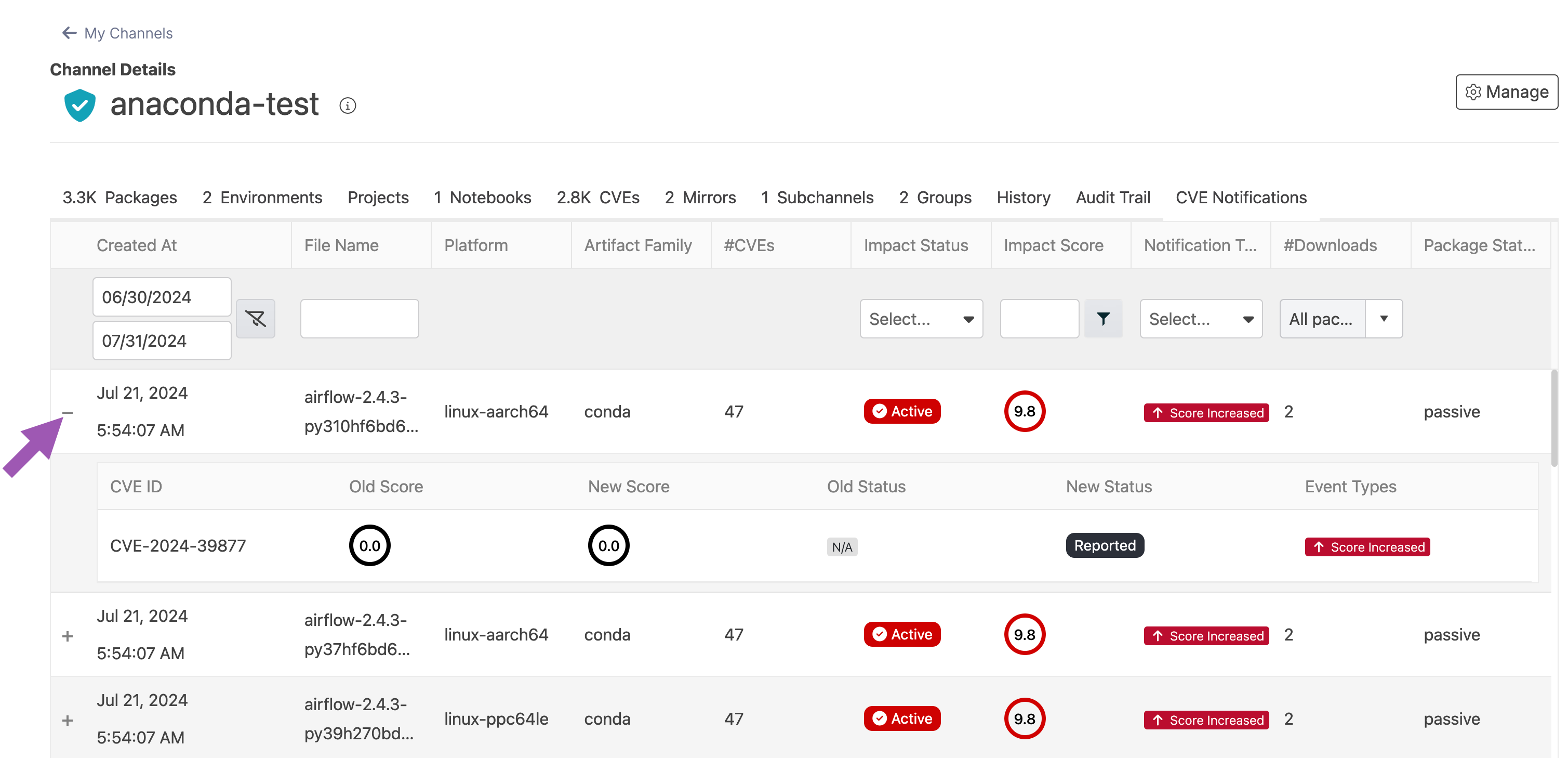 Use the date filter to narrow your timeline to locate a specific change in your channel.
Use the date filter to narrow your timeline to locate a specific change in your channel.
Why trust Anaconda?
Anaconda regularly pulls its CVE databases from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to minimize the risk of vulnerable software in our applications and web pages. Anaconda has an extensive and well-established process for curating CVEs, assessing whether or not packages Anaconda built are affected by any CVEs, determining which versions in our repository are affected, and mitigating the vulnerability.Understanding CVEs
Here’s what you need to know to make the right decisions regarding CVEs for your organization:Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
Standards for determining the severity of a CVE have evolved systematically through multiple iterations. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), established in 1999, provides a standardized mathematical framework for quantifying vulnerability characteristics. Following its initial implementation, CVSS 2.0 was released in 2007, introducing a structured metric-based approach. The framework underwent significant refinement in 2015 with CVSS 3.0, which incorporated enhanced contextual factors to more accurately reflect real-world vulnerability impact. In 2023, CVSS 4.0 was released, providing a comprehensive redesign that addresses contemporary security challenges. This latest version implements an expanded nine-metric base scoring system. CVSS 4.0 also provides improved assessment capabilities for modern deployment architectures, including cloud environments, containerized applications, and supply chain dependencies.CVE scores
Software developers refer to CVE databases and scores to minimize the risk of using vulnerable components (packages and binaries) in their applications or web pages. CVE scores and ratings fall into one of 5 categories:
CVE curation
Each CVE undergoes a rigorous curation process that evaluates its impact on packages in our repository. Each curated package receives additional metadata detailing the nature of the CVE, a package signature, and a CVE status. A checkmark next to a CVE score indicates that the CVE has undergone curation.Because packages can be affected by multiple CVEs, a single curated CVE does not guarantee a package is fully secure. If multiple CVEs exist for a package, ensure that each CVE is either cleared, mitigated, or otherwise determined to be non-impactful.
CVE statuses
CVEs are assigned a status category as a result of the Anaconda curation process. CVE status categories include:- Reported: The vulnerabilities identified in this package have been reported by NIST but not reviewed by the Anaconda team.
- Active: The vulnerabilities identified in this package are active and potentially exploitable.
- Cleared: The vulnerabilities identified in this package have been analyzed and determined not to be applicable.
- Mitigated: The vulnerabilities identified in this package have been proactively mitigated in this build through a code patch.
- Disputed: The legitimacy of the vulnerabilities identified in this package is disputed by upstream project maintainers or other community members.
To view this information in Package Security Manager, click the information icon beside CVE Status in the channel or package views.
CVE implementation
CVEs have a dedicated channel in Package Security Manager. This channel pulls from the repo.anaconda.cloud repository, which is updated every four hours. Activating your license automatically creates a mirror of this channel that runs hourly to synchronize between the channel repository and the local database.Air-gapped networks receive up-to-date CVEs and packages during the initial installation of Package Security Manager, and can update at regular intervals as desired. CVEs are updated daily for air-gapped users, and packages are updated monthly. See Updating CVEs and packages on an air-gapped network.
Viewing CVEs by channel
CVE views are only available to users whose role provides
Read permissions for the CVE category.
Filtering channel CVEs
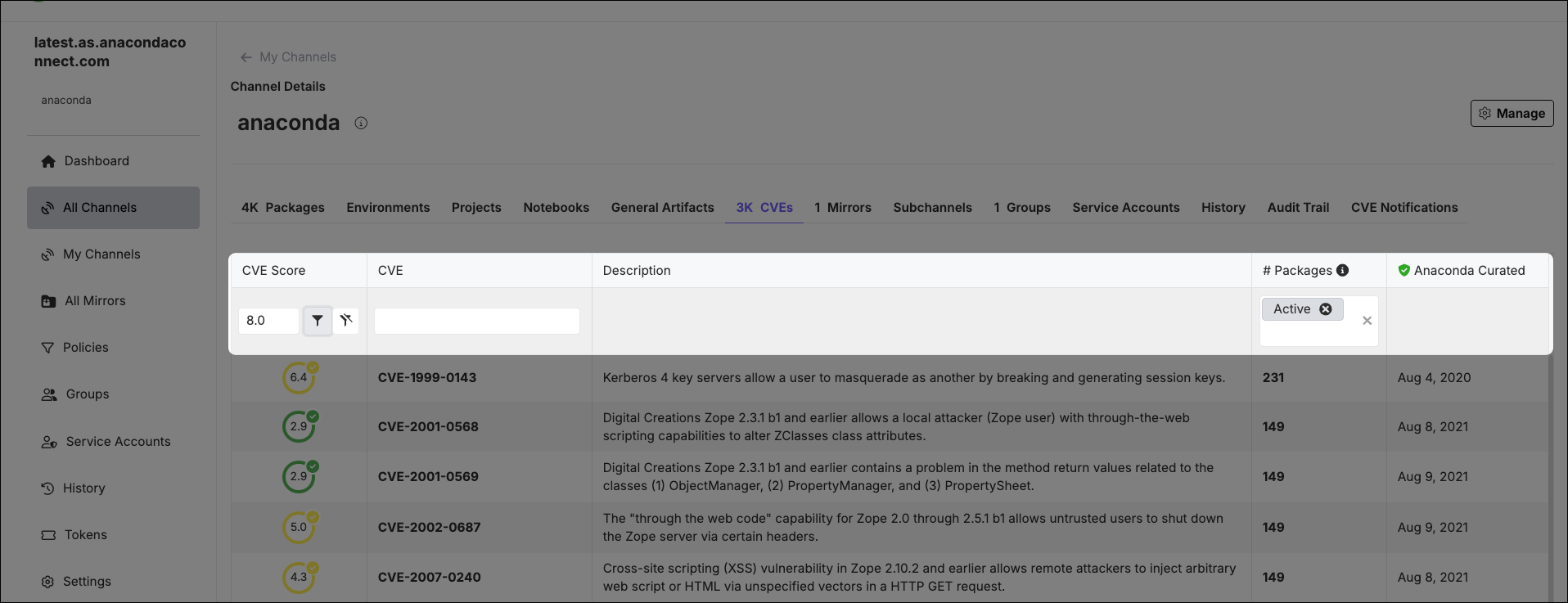
Apply filters to your channel’s CVEs tab by utilizing the fields at the top of the table columns. You can filter by:-
CVE Score
- Enter a number into the field to set the CVE Score threshold.
- Click the filter icon to open a dropdown menu and select an operator to use for the CVE Score threshold you entered. You can select Is greater than or equal to, or Is less than or equal to.
-
CVE Name
- If you know the name of the CVE you want to filter by, enter it in the search box. Only one CVE name can be entered at a time.
-
CVE Status
- You can filter CVEs by their Status using the # Packages column filter. Open the dropdown and select a CVE Status to filter the list of packages associated with the CVE to those that have the currently selected status.
Click the icon beside CVE Status to view more information about CVE statuses and what they mean.
More than one status can be selected at once. Click on the number in the column to view a list of packages associated with the CVE that have the currently selected status.

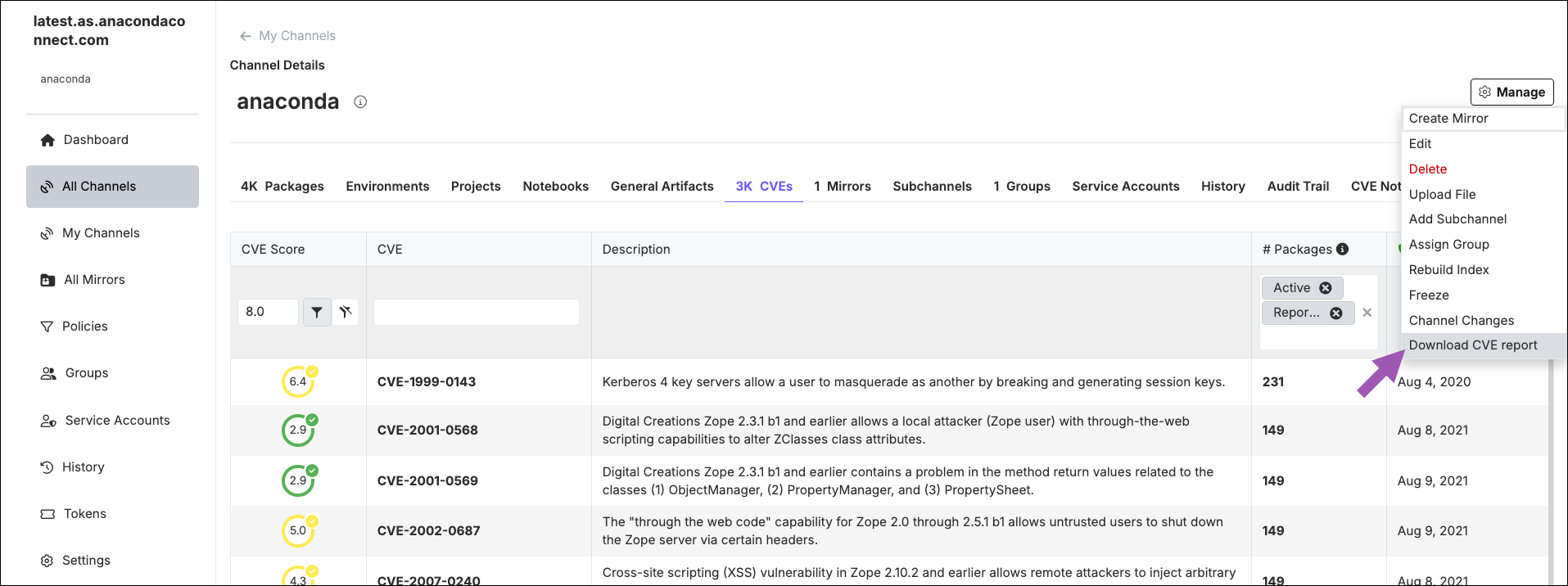
Downloading CVE reports
CVE reports provide a comprehensive list of CVEs associated with the packages in a channel in a.csv file.
To download a CVE report, open the channel’s Channel Details page, open the Manage dropdown, and select Download CVE Report. A notification displays to confirm that the report has been initiated. If you have applied filters to the channel’s CVE list, the report will contain filtered results.
For example, if you want a report containing a list of all the packages that pass your security threshold of “CVE score less than or equal to 8.0”, but still have an active or reported CVE, enter 8 as the CVE Score, adjust the filter to less than or equal to, select the Active and Reported statuses in the # Packages column, and then download the report.

Once a report has been initiated, it must complete before another report can be generated.
Viewing CVEs by package
Every channel’s packages list displays a # CVEs column indicating how many CVEs are associated with each package in the channel.The packages list is the default view when you open a channel.
- CVE Score
- Select the filter icon to open the filter menu and select the operator you want to use for the CVE Score. You can select either greater than or equal to, or less than or equal to.
- CVE Name
- If you know the name of the CVE you want to filter by, enter it in the search box. Only one CVE name can be entered at a time.
- CVE Status
- You can filter CVEs by their Status using the # Packages column filter. Open the dropdown and select a CVE Status to view the number of packages associated with the CVE that have the currently selected status.
- Anaconda Curated Date
- Select a start and end date to filter CVEs by the date they were curated by Anaconda.
- Last Modified Date
- Select a start and end date to filter CVEs by the date they were last modified.
- Last Published Date
- Select a start and end date to filter CVEs by the date they were last published.

Hover your mouse pointer over the CVE Score to view the various CVSS version scores for the CVE.

Viewing CVE details
Click on a CVE from any page to view detailed information about the CVE and its dangers. You can view a list of package files associated with the CVE, its CVE Status, and which platforms the package applies to. Select a CVSS tab to view the CVSS version information, which includes exploitability and impact metrics, along with the publication date by NVD and the curation date by Anaconda (if applicable).

The CVSS4 tab is not visible for Package Security Manager versions 6.7.x and older. However, if a package has CVSS4 scoring information, it is still visible in older version of Package Security Manager in the package file’s metadata. For more information, see Viewing file metadata.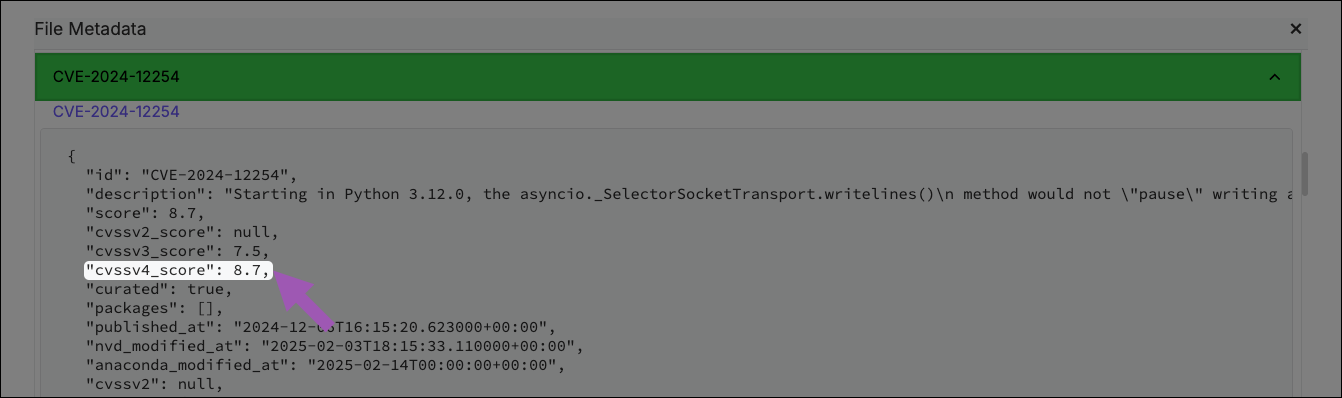

Searching for CVEs
You can search for CVEs using the search box at the top of the page. Open the filter dropdown menu, select CVEs, and then enter the name of the CVE you’re looking for in the search box.
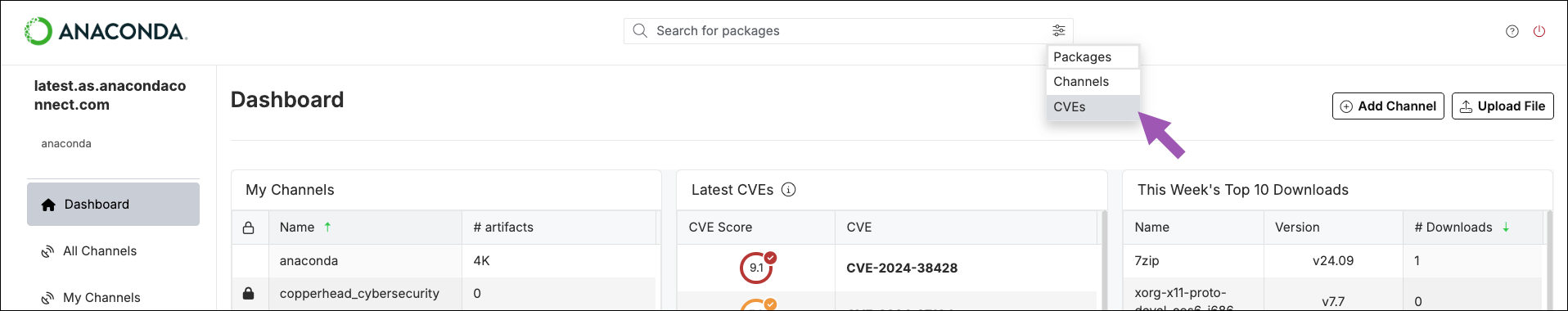
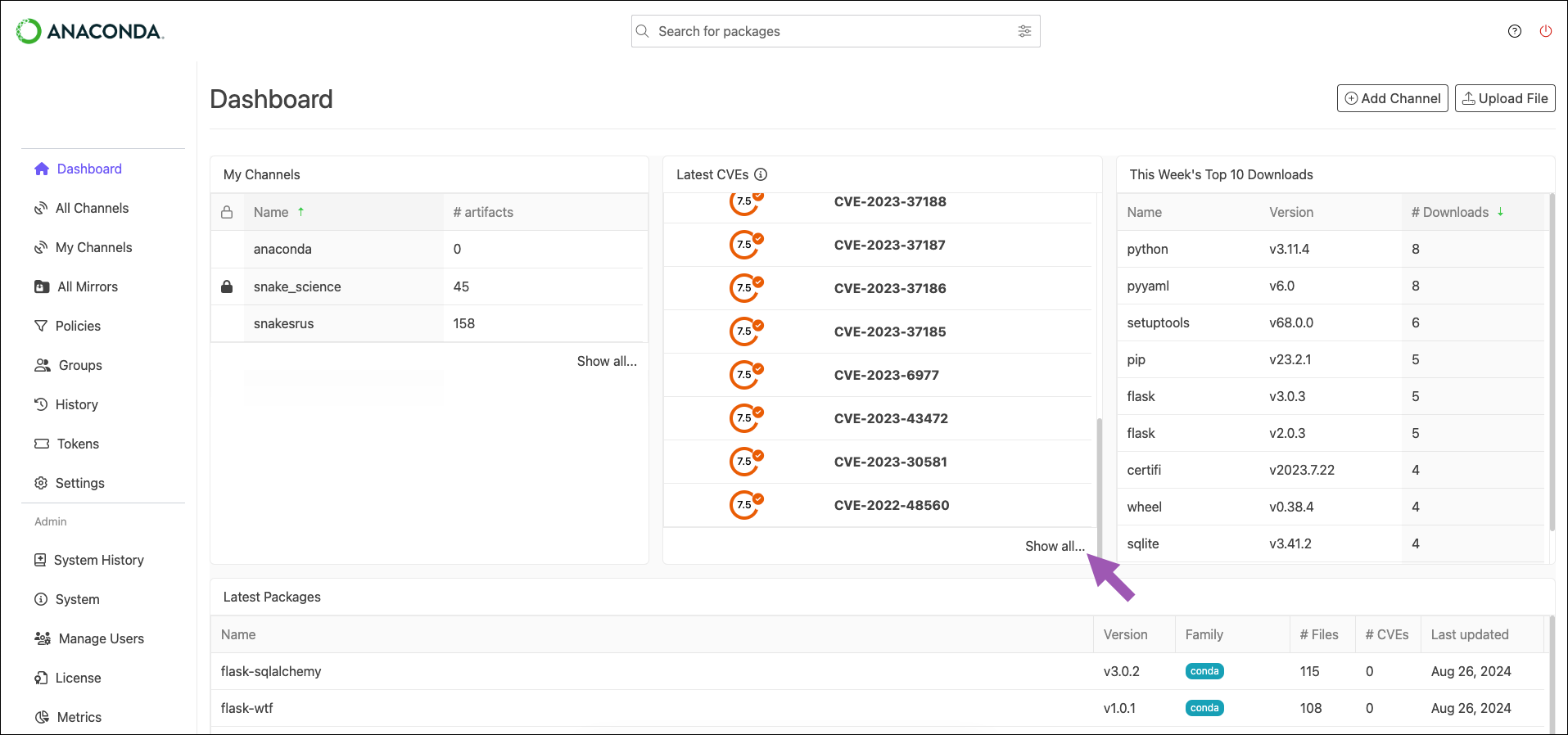
Listing the latest CVEs
The latest CVEs are always listed on the dashboard. To view a complete list of CVEs, click Show all… at the bottom of the CVE column. From this view, CVEs are sorted by their Anaconda Curated date, followed by published CVEs that still require curation.
CVE notifications
Hundreds of new CVEs are received by NVD daily. Because of this, our CVE mirror runs every four hours to keep itself, and you, up to date. CVE notifications provide administrators with alerts and updates regarding newly emerged CVEs or updated CVE scores that affect packages within a channel in Package Security Manager. Notifications are triggered based on a configurable CVE Score threshold. You can receive channel notifications for the following CVE events:- CVE score increase (based on set CVE Score)
- CVE score decrease (based on set CVE Score)
- CVE status change (active, cleared, mitigated)
7.0, you will receive notifications whenever a package score increases to 7.0 or higher, or if a package score is reduced to 6.9 or lower.
You will also receive notifications if a package score that already exceeds your threshold increases further. For example, you will receive a notification if a package score of 7.1 increases to 7.8.
To view a channel’s CVE notifications:
From the channel details page, select the CVE Notifications tab. Expand a notification to view the full details of the CVE changes.


The maximum range for the date filter is one year.
Managing CVEs using the CLI
For information on managing your CVEs using the CLI, see Package Security Manager CLI.Managing CVEs using the API
You can also use the API to list and view details about CVEs. Access the API interface by opening a browser and navigating tohttp(s)://<FQDN>/swagger/ui, replacing <FQDN> with your Package Security Manager fully qualified domain name.
The following is a list of available endpoints you can use to list and view CVEs in Package Security Manager:
Listing CVEs
Viewing CVE details
Updating CVEs and packages on an air-gapped network
Anaconda provides.zip files through Amazon Web Services (AWS) Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets. You can download the files you need on a allowlisted workstation with access to the internet, then move the files to the air-gapped network. Your public IP address is initially allowlisted during installation of Package Security Manager. If you need to allowlist a new IP address, contact Anaconda technical support.
- Download the package and CVE files you want to update.
- Move the downloaded package and CVE files to their correct location within your file system.

