Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
These instructions refer to Anaconda Distribution exclusively, but will also work with Miniconda.
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a free, cross-platform source code editor that works with Anaconda Distribution and Miniconda. Installing the Python for Visual Studio Code extension enables VS Code to connect to a conda environment’s version of Python as an interpreter for your Python code files.
More of a visual learner? Sign in to Anaconda.com and enroll in our Get Started with Anaconda course. See the Create a simple Python program with VS Code lesson in the Hands-on Practice section.
Launching VS Code in Navigator
With VS Code installed, you can launch the application from Navigator 1.9.12 or later by clicking the VS Code tile on the Home page.
When you launch VS Code from Navigator, it will automatically use the Python interpreter in the currently selected environment.
Creating a conda environment in VS Code
Before starting your Python project, Anaconda recommends creating a conda environment to isolate your project’s software packages and manage their dependencies.
You must have the Python for Visual Studio Code extension installed to create new conda environments from within VS Code on Windows.
- Open the Command Palette by pressing Ctrl+Shift+P (Windows, Linux)/Cmd+Shift+P (Mac).
- Select “Conda Creates a `.conda` Conda environment in the current workspace.”
- Select the Python version you’d like install in the environment.
Alternatively, you can create a new environment with Anaconda Prompt (Terminal in macOS/ Linux), and then select the environment in VS Code as the workspace’s Python interpreter.
For more information about managing environments with conda, see the official conda documentation.
For more information about Python environments in VS Code, see the official VS Code documentation.
Selecting Anaconda as a Python interpreter
Now that your conda environment has been created, select the environment as an interpreter. This ensures that your code has access to the correct code completion and type information available in the specific Python version and packages installed in your conda environment.
- Open any Python file.
- To select a Python interpreter, open the Command Palette by pressing Ctrl+Shift+P (Windows, Linux)/Cmd+Shift+P (Mac).
- Click Python: Select Interpreter in the Command Palette and select the interpreter associated with your Anaconda environment.
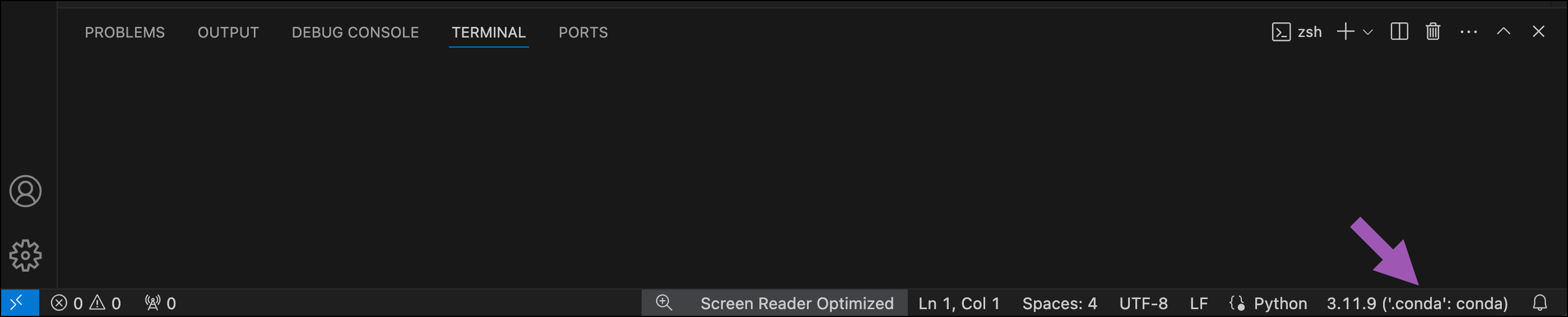
Anaconda interpreter typically appears as Python. 3.x.x (<YOUR_ENV_NAME>: conda). If your environment’s interpreter does not appear in the Select Interpreter list, click Refresh.
You can also manually enter an interpreter path by selecting Enter interpreter path….
For more information on finding a specific interpreter path in your Anaconda installation, see Finding your Anaconda Python interpreter path.
The selected interpreter displays in the bottom right corner of the status bar in VS Code.
Adding packages to your environment
To add packages to your environment in VS Code:
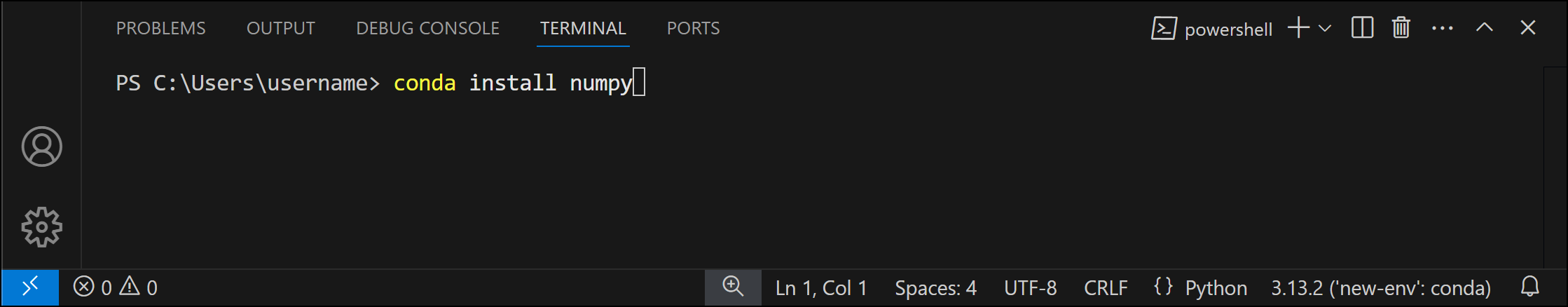
- Open a new terminal by pressing Ctrl+`.
- Run the following command:
On Windows, you can run conda commands in both Powershell and Command Prompt terminals in VS Code.
When you select the new environment, you may see a notification that says, “Selected conda environment was successfully activated, even though ‘(.conda)’ indicator may not be present in the terminal prompt.” You can still run conda commands in the terminal. See VS Code’s official documentation for more information on activating environments in terminal.
Learn more about adding conda packages to environments.
Testing your setup
You are now ready to execute your Python functions in VS Code!
-
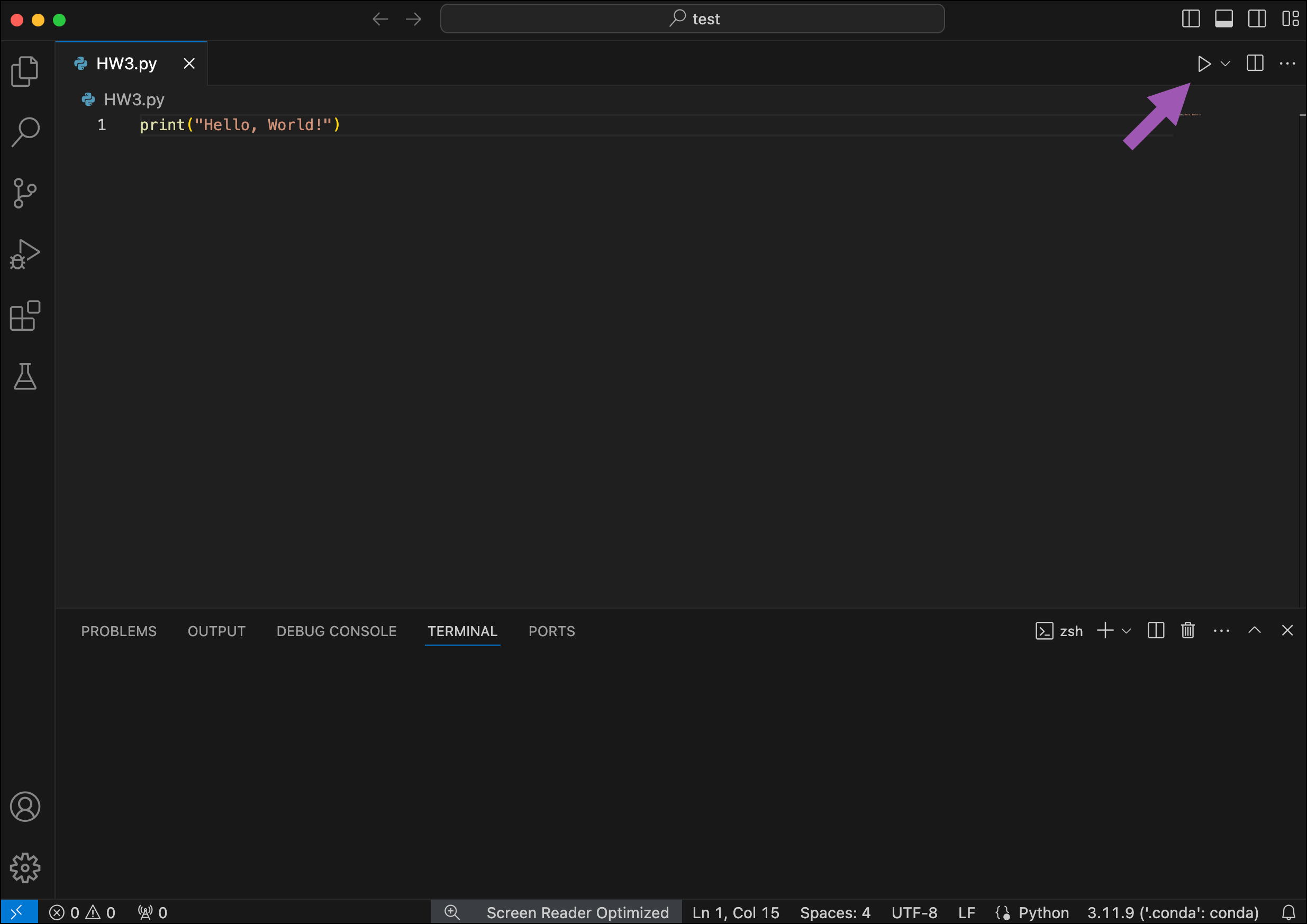
Create a new Python (.py) file.
-
Add the following code to your file:
-
Save the file.
-
Click Run Python File.
For more information on working with Python in VS Code, see Python in Visual Studio Code.

