Open source software powers the data science and AI revolution, providing the essential tools that researchers, developers, and organizations rely on daily. At Anaconda, we don’t just use open source—we’re actively building its future. In 2024 alone, our teams contributed thousands of commits across dozens of critical projects that millions of Python users depend on. As we look toward 2025, we’re doubling down on our commitment with ambitious plans to make these tools faster, more accessible, and more powerful.
This post offers a behind-the-scenes look at what we’ve accomplished and where we’re headed next—showcasing how Anaconda’s investment in open source is helping to shape the future of computational tools for everyone.
Our Open Source Legacy and Vision for Democratizing AI
Over the last decade, Anaconda has invested tens of millions of dollars in open source innovation through employee time, direct donations, event sponsorships, and more. This commitment has been integral to our growth and success, with some of our projects – like conda – dating back more than 12 years ago (conda’s first commit was on Oct. 15, 2012).
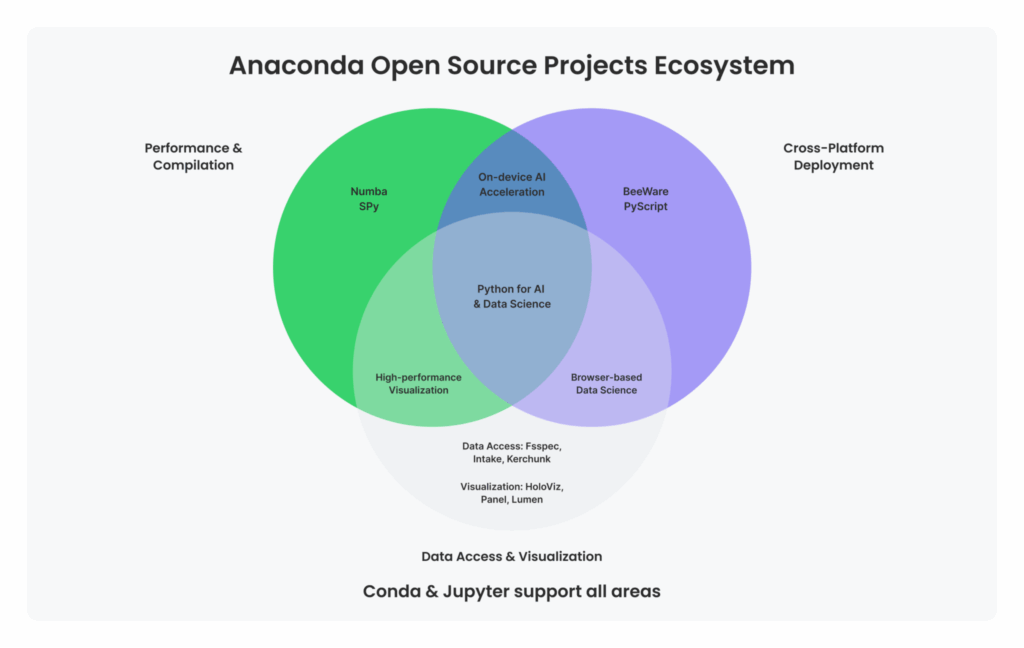
We believe that open source collaboration creates the strongest foundation for AI innovation, with our full-time engineers tackling complex, sustained work that strengthens the infrastructure millions of developers rely on daily. These contributions give us firsthand insights that drive improvements to projects including BeeWare, PyScript, conda, Jupyter, fsspec, Intake, Numba, SPy, Holoviz, Panel, and Lumen.
The scale of our impact is remarkable:
- conda-forge now maintains over 27,000 packages serving as the backbone of the Python scientific ecosystem
- fsspec and s3fs have become two of the top 20 libraries on PyPI with both getting over 300 million downloads per month
Anaconda’s Open Source Impact: Top PyPI Packages
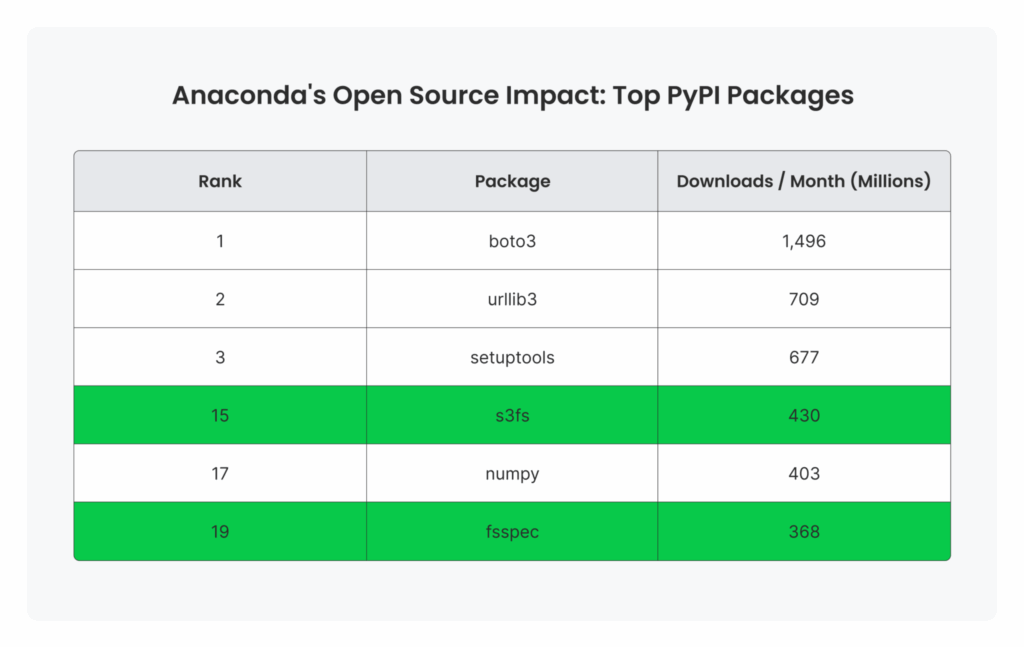
Source: pypistats.org on 2025-03-31
- Numba-accelerated code has enabled scientific applications to run up to 100x faster
- BeeWare helped Python on mobile reach a significant milestone with the first official wheels for iOS and Android
While AI continues to transform industries worldwide, these foundational open source tools are becoming increasingly critical infrastructure. The community-driven approach allows for more resilient software, faster innovation cycles, and broader adoption than any single organization could achieve alone. In contrast to the growing trend of proprietary AI models and closed ecosystems, our continued investment in open source tools provides a crucial counterbalance—preserving an environment where innovation remains accessible to all, knowledge is shared freely, and the barriers to entry for cutting-edge technology continue to fall.
Our Strategic Focus Areas
Anaconda’s open source initiatives form a coherent strategy aimed at addressing the most pressing challenges in AI, data science, and scientific computing:
- Performance bottlenecks that slow down computation-intensive tasks
- Platform constraints that restrict where Python can run
- Fragmented approaches to data access that add complexity
- Gaps in interactive computing and visualization that make insights harder to discover
By systematically addressing these challenges, we’re building a future where Python serves as a complete ecosystem for AI development—one that’s fast enough for demanding models, accessible to beginners, and deployable anywhere from cloud servers to mobile devices. These coordinated efforts strengthen Python’s position as the foundation for modern AI, enhancing its performance and capabilities across the entire data workflow.
Jupyter: Advancing the Interactive Workbench for Data Science and AI
Jupyter notebooks serve as the primary workspace where AI innovations begin. As a General Member of the Jupyter Foundation, Anaconda has strengthened this ecosystem through several key initiatives:
- Enhanced data accessibility: We developed the Jupyter-fsspec extension for seamless access to both local and cloud data sources
- Legacy support: We’ve maintained nbclassic for users relying on the traditional interface
- Community engagement: We’ve led bug triaging and documentation improvements
- Security leadership: We’ve strengthened practices through active participation in the Security Working Group
For 2025, our roadmap focuses on four areas of improvement:
- Modernizing the Gator Jupyter extension for enhanced conda environment management
- Integrating these capabilities directly into the notebook experience for Anaconda users
- Improving the developer experience with better documentation and a more reliable build system
- Collaborating on formal security advisory policies with clear incident response procedures
These enhancements are making Jupyter the de facto standard for interactive computing in science, education, and AI. By improving its usability, security, and integration with other tools, we’re democratizing data science and AI for millions of users worldwide.
Conda: The Foundation for Reproducible Environments
Conda serves as the essential package management system that powers the Anaconda Distribution, ensuring reproducible environments for AI development. It’s the infrastructure that allows data scientists to share environments with confidence, knowing their code will run consistently across different systems—critical for collaborative AI research and production deployments.
Our recent achievements include:
- Customizable channels: Implementing default channel configurations for different distribution providers
- Enhanced reporting: Adding plugin hooks for reporter backends, enabling customized output formats
- Specification support: Incorporating CEP-17 for Python package paths and CEP-20 for architecture-specific packages
For 2025, our primary focus is on solving critical pain points around environment management and reproducibility:
- Developing comprehensive improvements to streamline how developers define environments and preserve their state
- Creating a standardized conda-lock file format through a new CEP to significantly improve environment reproducibility across all conda-based tools
- Redesigning conda’s installation and startup behavior to prevent users from accidentally breaking their base environment
Conda has become the backbone of reproducible scientific computing environments across academia, research, and industry. The standardized lock file format and environment safeguards will ensure that environments work consistently regardless of when or where they’re deployed, supporting the entire ecosystem.
BeeWare: Write Once, Deploy Everywhere
BeeWare is revolutionizing how Python applications run by enabling developers to build and distribute cross-platform native apps—including mobile apps on Android and iOS—while maintaining a single Python codebase.
Our team has achieved several milestones this year:
- Official platform support: Establishing Android and iOS as Tier 3 supported platforms in the official Python project through PEP 730 and PEP 738
- Mobile package distribution: Leading efforts to publish iOS and Android wheels on PyPI, making it possible to pip install packages directly on mobile devices. Read more in our recent blog post by Dr. Russell Keith-Magee on Bringing Python to iOS and Android
- Improved packaging: Releasing significant improvements to Briefcase, BeeWare’s packaging tool for creating standalone applications
Looking to 2025, we’ll continue working toward full platform support for Android and iOS:
- Collaborating with the Python community to enable direct downloads of Python for mobile from python.org for the Python 3.14 release
- Modernizing Anaconda and miniconda installers using expertise from the Briefcase project
- Expanding the mobile Python ecosystem with better tooling and documentation
Bringing Python to mobile platforms opens up new possibilities for developers and organizations. By making it possible to write once and deploy everywhere, BeeWare is extending Python’s reach beyond traditional environments, potentially unlocking more sophisticated data science and AI capabilities directly on mobile devices.
BeeWare Adoption Surges: Mobile Python Tools See Exponential Growth Since 2022
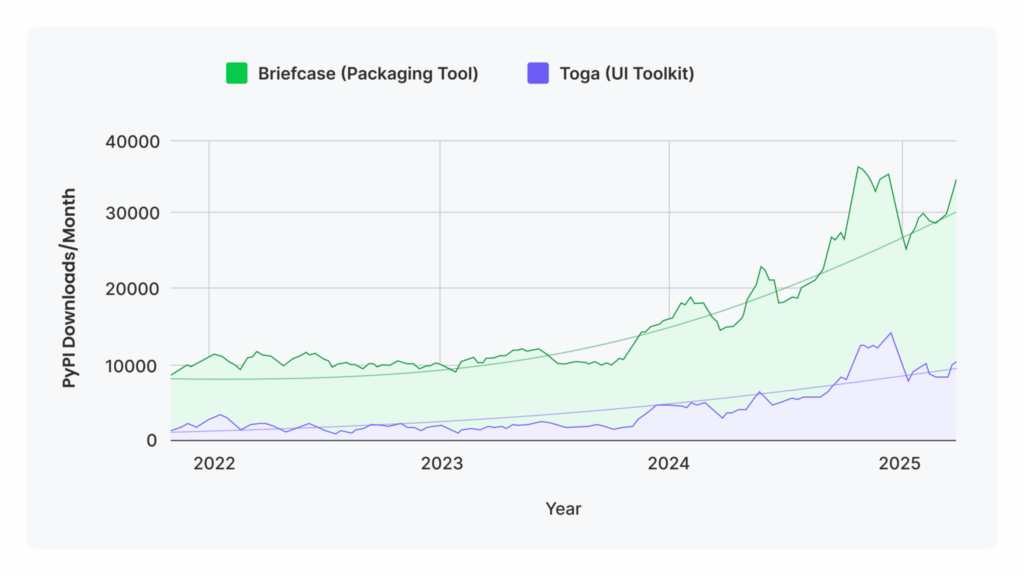
Source: Data collected using the pypistats library
PyScript: Python in Every Browser
PyScript transforms how Python runs on the web by bringing the complete language directly to browsers. Built on Pyodide and MicroPython, PyScript enables interactive Python applications without server-side dependencies—essentially bringing AI and data science capabilities to any device with a web browser.
We’ve made significant strides this year:
- Game development: Adding PyGame support for browser-based game development and interactive simulations
- Embedded improvements: Sponsoring enhancements to MicroPython for embedded devices
- Community building: Launching a newsletter (sign up at pyscript.net) and developing Invent for beginners learning programming
Our 2025 roadmap focuses on optimization and accessibility:
- Improving multi-threaded application performance by enhancing data transfer to web workers for parallel execution
- Expanding documentation and examples to lower the entry barrier for new developers
- Enhancing APIs to leverage upcoming Python features like Template Strings for building reactive front-ends
- Collaborating with the Fsspec team to create powerful data science applications that run entirely in the browser
PyScript democratizes Python by bringing it to the web. Now Python runs anywhere a browser runs–which is everywhere. This puts Python’s vast ecosystem of sophisticated computational tools within reach of anyone via just a simple URL, creating new possibilities for interactive learning, data visualization, and application development.
Fsspec and Intake: Universal Data Access
Anaconda maintains a suite of data access tools that solve various challenges in the modern data ecosystem. These tools work together to provide a comprehensive solution for accessing, cataloging, and processing data in any location and format – creating a universal bridge between AI applications and the data they need.
This year, we’ve expanded capabilities across several key areas:
- Universal interfaces: Enhancing fsspec as a universal interface to file storage in cloud environments
- Data catalogs: Improving Intake for seamlessly integrating diverse datasets
- Complex data handling: Continuing development of Akimbo for processing nested and ragged data
- Scientific data access: Releasing a Kerchunk version compatible with Zarr 3.0 for large datasets
- In-memory analytics: Adding DuckDB support to Akimbo for powerful analytics on complex structures
- High-energy physics: Completed dask-awkward, providing parallel-distributed processing of massive, complex datasets
For 2025, we’re focusing on enabling access to large datasets for web-based data science applications:
- Collaborating with the PyScript team to develop data streaming capabilities to web browsers
- Partnering with the HoloViz team to create dynamic visualizations of streamed data
- Enhancing integration between these tools for a seamless data access experience
Data access remains one of the most fundamental challenges in data science and analytics. By creating a unified ecosystem of tools that work across different storage systems, data formats, and computing environments, we’re removing barriers that traditionally slow down analytics workflows. The integration with web technologies through PyScript opens new possibilities for building interactive, browser-based data applications that can work with large datasets without requiring complex server infrastructure.
Numba and SPy: Putting Python Performance Within Reach
Numba transforms Python from an interpreted language into a high-performance computing powerhouse. It translates Python functions to optimized machine code at runtime using the industry-standard LLVM compiler library. By adding simple decorators to Python functions, developers can achieve performance that approaches compiled languages like C without changing their workflow. Complementing this, we’re developing SPy, a variant of Python designed specifically to simplify compilation, while preserving ease of use.
We’ve made significant progress this year:
- Core optimizations: Improving Numba’s compilation pipeline for better performance
- GPU support: Laying the groundwork for Numba 2.0 with enhanced NVIDIA CUDA support, enabling GPU-accelerated computing for AI, data science, and machine learning workloads
- Infrastructure improvements: Modernizing our continuous integration for more robust testing
- Language innovation: Advancing SPy as a performance-oriented alternative to Python
In 2025, we’ll focus on:
- Releasing Numba 2.0 with comprehensive GPU support for scientific computing and AI model development
- Expanding SPy language features and compiler optimizations for both CPU and GPU targets
- Developing seamless interoperability with the Python ecosystem
Performance remains a critical factor in scientific computing, data analysis, and AI workloads. By making high-performance computing accessible through Python-compatible tools like Numba and SPy, we’re democratizing access to computational speed that was previously available only to those with expertise in low-level languages. This work directly impacts researchers’ and organizations’ ability to process larger datasets, run more complex simulations, and develop more sophisticated models without specialized hardware programming knowledge.
HoloViz: Democratizing Data Visualization
HoloViz provides a set of Python packages that make data visualization easier, more accurate, and more powerful. This ecosystem includes libraries like Panel, Lumen AI, hvPlot, and more, working together to create a comprehensive visualization toolkit for data scientists and analysts.
We’ve made significant progress this year:
- AI-powered visualization: Releasing Lumen AI, which generates SQL queries, analyzes datasets, and builds visualizations without requiring code (read more about Lumen here)
- Enhanced interoperability: Improving connections between HoloViz components for consistent data storytelling
- Expanded capabilities: Extending visualization options across various data science workflows
For 2025, we’re focusing on three key areas:
- Enhancing Lumen AI for enterprise use cases by improving connections to production databases and data lakes
- Releasing new Panel widgets built on Material UI to bring consistent design and theming to the ecosystem
- Expanding support for modern DataFrame libraries like Polars and DuckDB throughout HoloViz
- Adopting Narwhals as a common interchange format in Bokeh to enable wider library support
Data visualization is essential for deriving insights and communicating results in data science. The HoloViz ecosystem democratizes these capabilities, making them accessible to users with varying levels of programming expertise. With Lumen AI’s code-free interface and Panel’s web-based dashboards, we’re enabling more people to create sophisticated, interactive visualizations without deep technical knowledge.
Looking Forward: Join Us in Shaping the Future
As we look ahead to 2025, Anaconda remains deeply committed to the open source Python ecosystem that powers data science, AI, and scientific computing worldwide. Our work spans the entire stack—from improving core infrastructure with Conda and Numba to expanding Python’s reach through PyScript and BeeWare. We’re particularly excited about bringing advanced data visualization capabilities to more users through HoloViz and connecting the dots between cloud data access and interactive computing through our Jupyter and fsspec integrations.
By focusing on performance, cross-platform support, and intuitive interfaces, we’re strengthening the foundations that make Python the language of choice for everyone from students to research scientists to enterprise data teams,
It is through community involvement that these open source ecosystems thrive. We invite you to learn more about Anaconda’s open source commitment and get involved. Whether you’re reporting bugs, improving documentation, contributing code, or simply spreading the word, your participation helps make these tools better for everyone. The future of open source at Anaconda isn’t just about what we build—it’s about what we all build together.
Dan Yeaw is an OSS Engineering Manager at Anaconda, where he leads a team of OSS software engineers working on BeeWare, PyScript, Jupyter, fsspec, and more. His background is in complex systems engineering and safety in the automotive industry and the military, and is excited to bring those experiences to help build rigorous community-focused solutions to open source projects. Outside of work, he hosts Michigan Python and loves riding bicycles.